In modo, the affect any tool has upon a selected region of geometry is rigid, meaning applications of a tool happen at a constant rate across the selected range. modo provides a way to attenuate the affect a tool has over a selection as a Falloff, a gradual decrease in intensity across a defined range. Falloffs are universal in application, once activated they are persistent until disabled, and work with all the various tools. As a matter of fact, many tools are simply pre-made combinations of a specific Falloff and a transform; add the Rotate tool to a Linear Falloff and get a Twist tool. This is made possible using the power of the Tool Pipe.
Defining Falloffs is done by selecting the type of Falloff desired form the drop down menu either within the interface, in the 'Falloff' selector menu or in the menu bar under "Edit > Falloff".
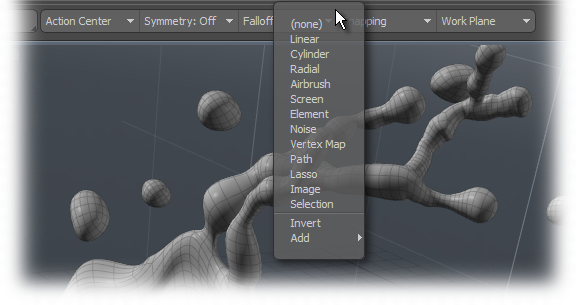
Once selected, users may LMB+ click and drag in the viewport to define the range. Taking its position cue from the Work Plane, the first click defines the origin or center of the Falloff, and the drag action defines the size or range. Release the mouse button to accept the Falloff, and any subsequent tool applications will utilize the Falloff until it is disabled by selecting 'none'. When a Falloff of is active, its properties are visible within the tools properties panel, as an adjunct to the tools properties itself. Each has its on specific settings. Anytime a tool is in interactive mode, users can modify the input values and receive real-time feedback of the results. Additionally, users may adjust the tool directly in the viewport by LMB+click dragging the widgets visible on the Falloff display.
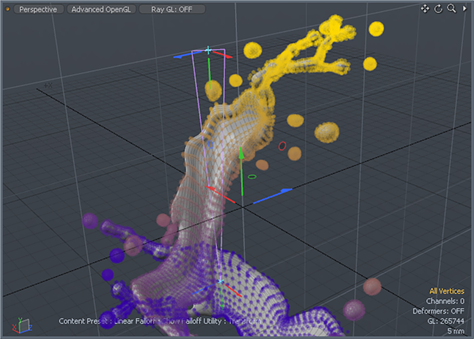
If a tool is active when setting a Falloff, such a the move or rotate tools, the act of simply selecting the Falloff type in the menu will automatically scale the Falloff to the bounding box size of the active selection (which would be all geometry if nothing were selected). This functionality makes it easy to accurately apply Falloffs when modeling. To better visualize the effect a Falloff has over a selection, users can enable the 'Show Falloffs' option in the menu bar under "View > Show Falloffs". This colorize's the vertices depending on the amount of influence a Falloff has over them, dark purple for no influence transitioning toward yellow for full influence as demonstrated by the image below (with a Linear Falloff on the Y axis).
Falloff Types
Linear
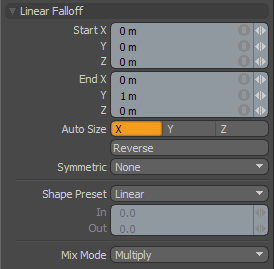 Linear Falloff uses a straight line to define Falloff. The line itself determines the direction of the Falloffs influence with the strength of the effect itself reaching out toward infinity. All the vertices at one end of the line receive 100% of the tool's influence. The vertices at the other side receive 0% of the tool's influence. The points between the two lines receive some partial value based on the interpolation between the two end points.
Linear Falloff uses a straight line to define Falloff. The line itself determines the direction of the Falloffs influence with the strength of the effect itself reaching out toward infinity. All the vertices at one end of the line receive 100% of the tool's influence. The vertices at the other side receive 0% of the tool's influence. The points between the two lines receive some partial value based on the interpolation between the two end points.
Start X/Y/Z: Defines the starting position of the Falloff as a specific XYZ coordinate value. This end of the line and everything beyond it receives the maximum amount of influence attenuating toward the 'End' position.
End X/Y/Z: Defines the end position of the Falloff as a specific XYZ coordinate value. This end of the line and everything beyond it receives no influence attenuating toward the 'Start' position.
Auto Size X/Y/Z: Users can select either of these three options to automatically scale the 'Start' and 'End' points of the Falloff to match the bounding box size of the selected elements along one of the three axes.
Reverse: Users can select this option to invert the 'Start' and 'End' points reversing the influence of the Falloff.
Symmetric: Users can choose from several options to automatically mirror the influence area of the Falloff-
None- Symmetric function is disabled
Start- Influence of Falloff is symmetrically mirrored across the 'Start' position.
End- Influence of Falloff is symmetrically mirrored across the 'End' position.
Shape Preset: The strength of the Falloffs influence can be controlled along the extent using a 'Shape Preset'-
Linear- Attenuation of Falloff occurs evenly across its range.
Ease-In- Strength of Falloff is greater toward the 'Start' position.
Ease-Out- Strength of Falloff is greater toward the 'End' position.
Smooth- Strength of Falloff is greater toward the center of the Falloff.
Custom- Users can use the 'In'/'Out' options to fine tune strength of Falloff.
In/Out: The 'In' value determines the strength of the Falloff nearer to the 'Start' position, where the 'Out' value determines the strength on nearer the 'End' side of the Falloff.
Mix Mode: In instances where there are multiple falloffs applied to a transform (using the 'Add' option of the Falloff menu), the mix mode defines how each Falloff interacts with the other.
Cylinder
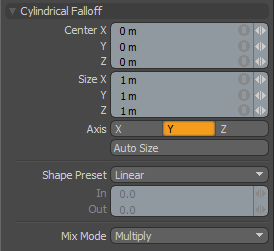 The Cylindrical Falloff creates a circular Falloff that extends across the length of a virtual cylinder. All vertices at the center of the cylinder receive 100% of the tools influence attenuated toward the outer edge and beyond the cylinder, where vertices receive none of the tools influence.
The Cylindrical Falloff creates a circular Falloff that extends across the length of a virtual cylinder. All vertices at the center of the cylinder receive 100% of the tools influence attenuated toward the outer edge and beyond the cylinder, where vertices receive none of the tools influence.
Center X/Y/Z: Defines the Center of influence, where the strength of the Falloff will be greatest (100%). The strength of the falloff will attenuate toward the outer bounds of the Cylinder. The Falloff volume extends upward and downward toward infinity.
Size X/Y/Z: Defines the radius of a perfect circle from the 'Center' and determines the outer area of the Falloff where there is no affect.
Axis: Defines the Projection Axis for the cylinder determining the direction for the Falloff.
Auto Size: Users can select this option to automatically size the Falloff's 'Center' and 'Size' values to match the bounding box of the current selection.
Shape Preset: The strength of the Falloffs influence can be controlled along the extent using a 'Shape Preset'-
Linear- Attenuation of Falloff occurs evenly across its range.
Ease-In- Strength of Falloff is greater toward the 'Start' position.
Ease-Out- Strength of Falloff is greater toward the 'End' position.
Smooth- Strength of Falloff is greater toward the center of the Falloff.
Custom- Users can use the 'In'/'Out' options to fine tune strength of Falloff.
In/Out: The 'In' value determines the strength of the Falloff nearer to the 'Start' position, where the 'Out' value determines the strength on nearer the 'End' side of the Falloff.
Mix Mode: In instances where there are multiple falloffs applied to a transform (using the 'Add' option of the Falloff menu), the mix mode defines how each Falloff interacts with the other.
Radial
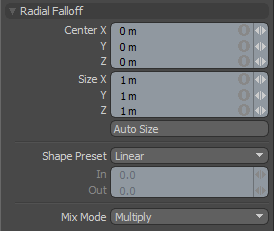 Radial Falloff uses a sphere where all vertices at the very center of the sphere receive 100% tool influence and any vertices outside the sphere receive 0% of the tool's influence. There is a smooth gradient of tool influence between the center and edge boundary of the sphere that utilizes the Falloff shape preset to determine the interpolation style.
Radial Falloff uses a sphere where all vertices at the very center of the sphere receive 100% tool influence and any vertices outside the sphere receive 0% of the tool's influence. There is a smooth gradient of tool influence between the center and edge boundary of the sphere that utilizes the Falloff shape preset to determine the interpolation style.
Center X/Y/Z: Defines the Center of influence, where the strength of the Falloff will be greatest (100%). The strength of the falloff will attenuate toward the outer bounds of the Spherical volume, the area outside the volume receives no tool influence.
Size X/Y/Z: Defines the radius of a perfect circle from the 'Center' and determines the outer area of the Falloff where there is no affect.
Auto Size: Users can select this option to automatically size the Falloff's 'Center' and 'Size' values to match the bounding box of the current selection.
Shape Preset: The strength of the Falloffs influence can be controlled along the extent using a 'Shape Preset'-
Linear- Attenuation of Falloff occurs evenly across its range.
Ease-In- Strength of Falloff is greater toward the 'Start' position.
Ease-Out- Strength of Falloff is greater toward the 'End' position.
Smooth- Strength of Falloff is greater toward the center of the Falloff.
Custom- Users can use the 'In'/'Out' options to fine tune strength of Falloff.
In/Out: The 'In' value determines the strength of the Falloff nearer to the 'Start' position, where the 'Out' value determines the strength on nearer the 'End' side of the Falloff.
Mix Mode: In instances where there are multiple falloffs applied to a transform (using the 'Add' option of the Falloff menu), the mix mode defines how each Falloff interacts with the other.
Airbrush
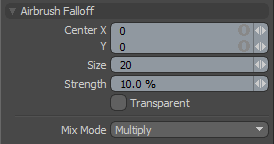 The Airbrush Falloff allows a tools influence to be painted onto a mesh. Unlike the other Falloff tools, airbrush continually adds to the tool influence while you drag the brush around the mesh. This tool is similar to the Airbrush tool found in 2D paint programs, except rather than smoothly painting pixels into an image, the brush paints the tool influence into the mesh. This can be combined with many tools in modo for a wide variety of effects. Users can RMB+click and drag to define the size of the brush being applied interactively.
The Airbrush Falloff allows a tools influence to be painted onto a mesh. Unlike the other Falloff tools, airbrush continually adds to the tool influence while you drag the brush around the mesh. This tool is similar to the Airbrush tool found in 2D paint programs, except rather than smoothly painting pixels into an image, the brush paints the tool influence into the mesh. This can be combined with many tools in modo for a wide variety of effects. Users can RMB+click and drag to define the size of the brush being applied interactively.
To use the 'Airbrush falloff, activate the Falloff, apply the effect, such a 'Move'. At first users will see no results, then LMB+click and drag over the surface of the model to apply the tools action to the geometry.
Center X/Y: Determines the current center position in the viewport of the brush tip, users can interactively LMB+click and drag over a models surface to actually apply the Falloff.
Size: Sets the pixel size of the Airbrush tips influence, calculated as a radius from the 'Center' position.
Strength: The 'Strength' value defines the intensity of the Falloffs application when brushing over a surface.
Transparent: When 'Transparent' is disabled, the Falloff only affect polygons facing toward the viewport, when enabled the falloff works through surface also affecting those facing away from the viewports.
Mix Mode: In instances where there are multiple falloffs applied to a transform (using the 'Add' option of the Falloff menu), the mix mode defines how each Falloff interacts with the other.
Screen
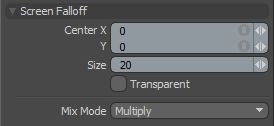 Screen Falloff is actually quite similar to Cylinder Falloff, except rather than using one of the major axes to determine the angle of the projection, the screen Falloff projects a cylinder that is perpendicular to the viewport window (i.e. the computers screen). The Falloff is defined by a disc drawn in screen space extending infinitely into the distance. This disc is used to project a virtual cylinder of influence.
Screen Falloff is actually quite similar to Cylinder Falloff, except rather than using one of the major axes to determine the angle of the projection, the screen Falloff projects a cylinder that is perpendicular to the viewport window (i.e. the computers screen). The Falloff is defined by a disc drawn in screen space extending infinitely into the distance. This disc is used to project a virtual cylinder of influence.
Center X/Y: Defines the Center of influence in screen space, where the strength of the Falloff will be greatest (100%). The strength of the falloff will attenuate toward the outer bounds of the Spherical volume, the area outside the volume receives no tool influence.
Size: Sets the pixel size of the Circular area of influence, calculated as a radius from the 'Center' position.
Transparent: When 'Transparent' is disabled, the Falloff only affect polygons facing toward the viewport, when enabled the falloff works through surface also affecting those facing away from the viewports.
Mix Mode: In instances where there are multiple falloffs applied to a transform (using the 'Add' option of the Falloff menu), the mix mode defines how each Falloff interacts with the other.
Element
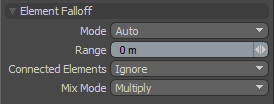 Element Falloff limits the tool influence to the element (vertex, edge or polygon) in the mesh that is clicked on when using the current tool. USers can hover the mouse pointer over a component (vertex, edge or polygon) and see a pre-highlight of the target elements. LMB+clicking on the element will apply the tools action to the element, attenuating outward based on the 'Range' value.
Element Falloff limits the tool influence to the element (vertex, edge or polygon) in the mesh that is clicked on when using the current tool. USers can hover the mouse pointer over a component (vertex, edge or polygon) and see a pre-highlight of the target elements. LMB+clicking on the element will apply the tools action to the element, attenuating outward based on the 'Range' value.
Mode: There are several modes available for selecting the element type-
Auto- Users can choose from any component, based on which element is clicked on.
Auto Center- Same as 'Auto', but the 'Range' is calculated from the elements center point.
Vertex- Users are limited to only selecting Vertices.
Edge- Users are limited to only selecting Edges.
Edge Center- Same as Edge', but the 'Range' is calculated from the elements center point.
Polygon- Users are limited to only selecting Polygons.
Polygon Center- Same as 'Polygon', but the 'Range' is calculated from the elements center point.
Range: This value determines the extent of the Falloff range, measured outward from the tool handle. When the 'Center' options are selected, the 'Range' is calculated from the elements center point. At the default 0m value, only the clicked element will be affected.
Connected Elements: Defines what connected geometry will do when an element is transformed.
Ignore- Ignores all connected elements and only moves the element specified.
Use Connectivity- Only affects single surface/connected elements, unconnected elements within range will be ignored.
Rigid Connections- Moves all connected elements equally the specified distance.
Edge Loops- Moves the connected loop, defined by all the connected quad polygons/edges/vertices in a single row.
Mix Mode: In instances where there are multiple falloffs applied to a transform (using the 'Add' option of the Falloff menu), the mix mode defines how each Falloff interacts with the other.
Noise
 Noise Falloff uses a three dimensional noise pattern to modulate the influence of the tool. The size of the noise pattern can be adjusted with the scale parameter. Combined with the Move or Stretch tool, this Falloff can be useful for roughing up a surface.
Noise Falloff uses a three dimensional noise pattern to modulate the influence of the tool. The size of the noise pattern can be adjusted with the scale parameter. Combined with the Move or Stretch tool, this Falloff can be useful for roughing up a surface.
Scale: This value determines the size of the noise in relation to the geometry it is affecting.
Mix Mode: In instances where there are multiple falloffs applied to a transform (using the 'Add' option of the Falloff menu), the mix mode defines how each Falloff interacts with the other.
Vertex Map
 The Vertex Map falloff converts values of the currently selected vertex map to values representing falloff strength. While generally a Weight Map is used, being the most intuitive approach, users may also use values of other vertex map types as a falloff as well. The Falloff is determined by the values of an existing vertex map.
This allows users the ability to create complex Falloffs that actually can have a inverse negative in instances where negative values can be applied.
The Vertex Map falloff converts values of the currently selected vertex map to values representing falloff strength. While generally a Weight Map is used, being the most intuitive approach, users may also use values of other vertex map types as a falloff as well. The Falloff is determined by the values of an existing vertex map.
This allows users the ability to create complex Falloffs that actually can have a inverse negative in instances where negative values can be applied.
If user chooses "Component" for the 'Mode' option, the falloff tool uses the component value specified by the index option. For example, if the current map is a Morph Map and the index is "X", then the falloff sets the X value of morph position to the weight value. "Magnitude" is effective for Morph, RGB, and RGBA maps. If the current map selected is a Morph map, the falloff returns the length of the morph delta position. If it is RGB or RGBA, the falloff returns the luminosity of color vector.
Mode:
Magnitude- Values of the vertex map are converted to strength values and applied to the affected surface(s).
Component- Users can select individual components of a map- Weight Map (1 component- weight value), RGB Map (3 components- R, G or B), RGBA Map (4 components- R, G, B or A), Morph Map (3 components- X, Y or Z), Pick Map (1 component)
Index: When 'Component' mode is selected, users determine the specific component using this option selector.
Mix Mode: In instances where there are multiple falloffs applied to a transform (using the 'Add' option of the Falloff menu), the mix mode defines how each Falloff interacts with the other.
Path
 The Path Falloff combines the Curve Generator with the Path Falloff. The curve generator creates a curve and the Falloff reads the curve points to determine where the tool should be active. If the user has the Path Falloff in the Tool Pipe at the same time as a mesh edit or transform tool, they may need to select the Curve Path (in 'Polygons' mode) prior to activating the Falloff. This will allow users to define the curve to be used. Once the basic curve created users can select the tool and begin to edit. Users may also click on the curve control points to edit them while the tool/Falloff combination is active.
The Path Falloff combines the Curve Generator with the Path Falloff. The curve generator creates a curve and the Falloff reads the curve points to determine where the tool should be active. If the user has the Path Falloff in the Tool Pipe at the same time as a mesh edit or transform tool, they may need to select the Curve Path (in 'Polygons' mode) prior to activating the Falloff. This will allow users to define the curve to be used. Once the basic curve created users can select the tool and begin to edit. Users may also click on the curve control points to edit them while the tool/Falloff combination is active.
Size: This value determines the area of attenuation around the path itself, calculated as a tube around the curves position.
Mix Mode: In instances where there are multiple falloffs applied to a transform (using the 'Add' option of the Falloff menu), the mix mode defines how each Falloff interacts with the other.
Lasso
 Several styles of Lasso selections drawn in screen space projecting outward toward infinity, producing Falloffs that are very specific.
Settings allow users to then to define areas of influence around the lasso shape with the 'Soft Border' option. All areas within the Lasso receive 100% of the tools effect; the attenuation of the falloff occurs across the 'Soft Border' distance only outside the Lasso area.
Several styles of Lasso selections drawn in screen space projecting outward toward infinity, producing Falloffs that are very specific.
Settings allow users to then to define areas of influence around the lasso shape with the 'Soft Border' option. All areas within the Lasso receive 100% of the tools effect; the attenuation of the falloff occurs across the 'Soft Border' distance only outside the Lasso area.
Style: Users can choose from the various Lasso styles-
Lasso- Allows users to draw freeform shapes onto the screen defining the Falloff .
Rectangle- Users can drag out rectangular shapes to define the Falloff area.
Circle- Users can drag out perfectly circular shapes to define the Falloff area. Shape originates from center of the circle.
Ellipse- Users can drag out elliptical shapes to define the Falloff area. Shape originates from the upper or lower corner of the ellipse.
Soft Border: The 'Soft Border' option defines the actual Falloff radius around the Lasso area that attenuates across the distance defined. Calculated in screen-space pixels from the lasso border.
Mix Mode: In instances where there are multiple falloffs applied to a transform (using the 'Add' option of the Falloff menu), the mix mode defines how each Falloff interacts with the other.
Image
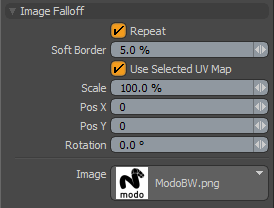 Much like the Image Ink option in the painting toolbox, users may apply an image, in screen space, as a Falloff, where the brightness (luminosity) of the image will affect the selected geometry. Additionally, by selecting the 'Use Current UV' option of the Falloff, users can apply the current image as a Falloff in 3D object space opening up a whole variety of options.
Much like the Image Ink option in the painting toolbox, users may apply an image, in screen space, as a Falloff, where the brightness (luminosity) of the image will affect the selected geometry. Additionally, by selecting the 'Use Current UV' option of the Falloff, users can apply the current image as a Falloff in 3D object space opening up a whole variety of options.
To use, user will need to place the masking image into the images folder of the Presets, or add the path to the Preset Browser. Once the image is selected, LMB+clicking in the viewport will activate the image widget, where users can use the controls to position the image within the 3D viewport using the various handles.
Repeat: When this option is enabled, the image is repeated outside of the images borders. Has no effect when 'Use Selected UV Map' is enabled.
Soft Border: Attenuates the strength of the images affect over the geometry. At 100% the strength of the falloff is strongest at the center falling off toward the edges of the image. At 0%, the white areas of the entire image will affect the geometry.
Use Selected UV Map: When this option is enabled, modo will bypass the viewport image, and apply the image's affect to the surface with the currently selected UV map. Users can select UV maps within the Lists viewport under the UV Map section.
Scale: This value determines the size of the image in the 3D viewport, and when 'Repeat' is disabled, the size of the Falloffs area of influence as well. USers can LMB+click the right side handle to interactively rotate the image.
Pos X/Y: Positions the center point of the Image within the 3D viewport. Users can also LMB+click the center handle on the widget to interactively position the image.
Rotation: Rotates the image within the3D viewport. Users can LMB+click the top handle to interactively rotate the image.
Image: Users can use the 'Image' button to browse through the preset bitmap textures, selecting the image that will be used for the Falloff.
Selection
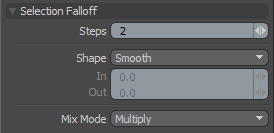 Selection Falloff allows you to modulate a geometry edit based on a selection area. The area of influence is at 0% on the selection border and ramps to 100% based on the Steps value. If the Steps are set to 1 there will be only a slight Falloff range at resulting in a "harder" edit. Increasing the number of steps will soften the influence at the selection border and the number of steps can be controlled by RMB (right mouse button), or by editing the text field in tool properties. You might think of these "steps" as rows or loops of selected elements; for each Step the Falloff reduces the selection area and uses the range between the original selection and the reduced selection as the "soft" border for the Falloff area.
Selection Falloff allows you to modulate a geometry edit based on a selection area. The area of influence is at 0% on the selection border and ramps to 100% based on the Steps value. If the Steps are set to 1 there will be only a slight Falloff range at resulting in a "harder" edit. Increasing the number of steps will soften the influence at the selection border and the number of steps can be controlled by RMB (right mouse button), or by editing the text field in tool properties. You might think of these "steps" as rows or loops of selected elements; for each Step the Falloff reduces the selection area and uses the range between the original selection and the reduced selection as the "soft" border for the Falloff area.
Steps: This value determines the extent of the Falloff range, where each 'Step' represents a loop of polygons or a ring of edge sections. The greater the 'Steps;' value, the further the Falloff attenuates.
Shape: The strength of the Falloffs influence can be controlled along the extent using a 'Shape Preset'-
Linear- Attenuation of Falloff occurs evenly across its range.
Ease-In- Strength of Falloff is greater toward the 'Start' position.
Ease-Out- Strength of Falloff is greater toward the 'End' position.
Smooth- Strength of Falloff is greater toward the center of the Falloff.
Custom- Users can use the 'In'/'Out' options to fine tune strength of Falloff.
In/Out: The 'In' value determines the strength of the Falloff nearer to the 'Start' position, where the 'Out' value determines the strength on nearer the 'End' side of the Falloff.
Mix Mode: In instances where there are multiple falloffs applied to a transform (using the 'Add' option of the Falloff menu), the mix mode defines how each Falloff interacts with the other.
TIP: Commands such as 'Copy', 'Paste' or 'Delete' are typically all or nothing type events and are therefore unaffected by Falloffs.


